Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
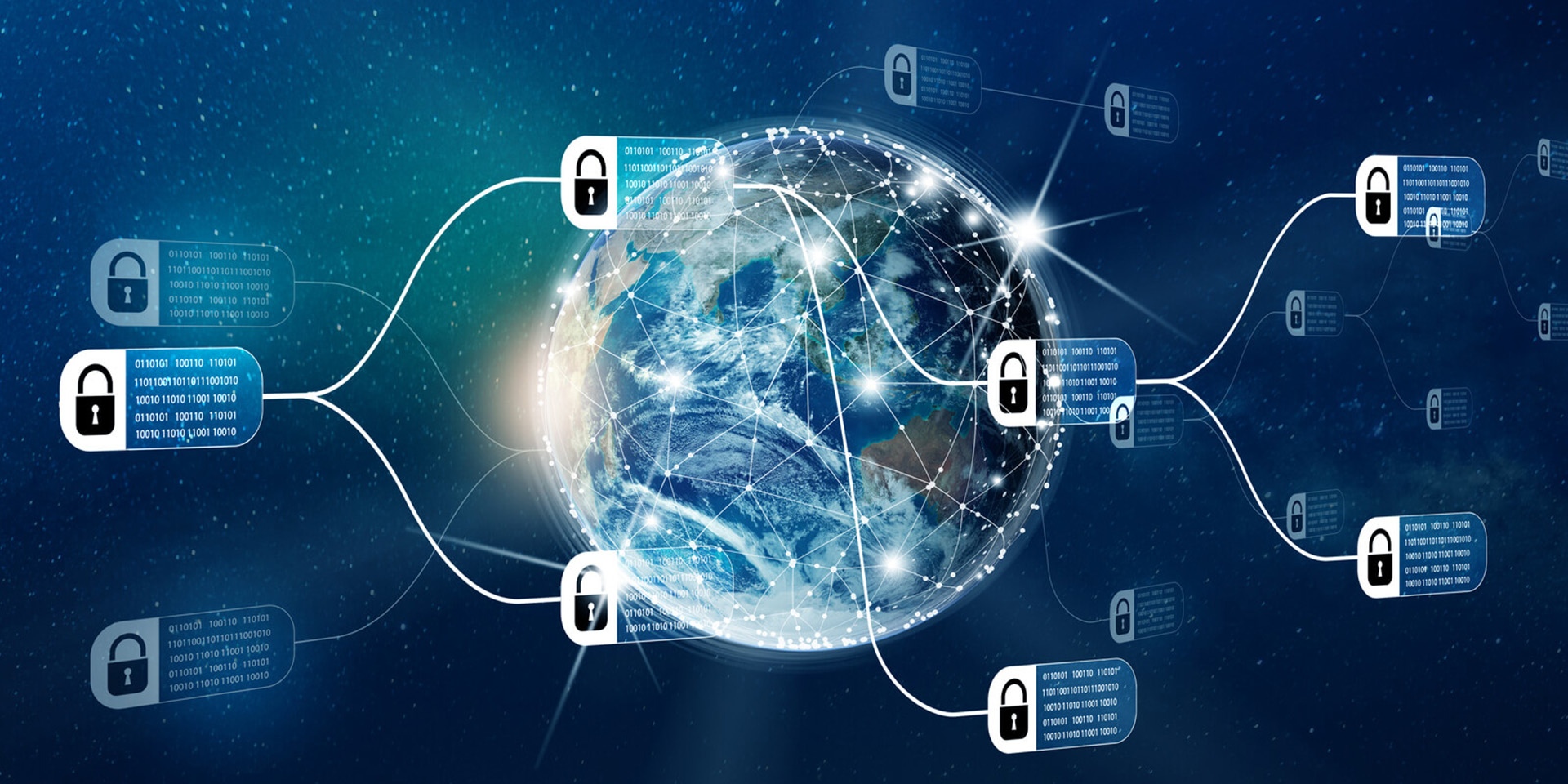

Explaining blockchain involves breaking down the complex technology that underpins cryptocurrencies and various decentralized applications. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered data cannot be altered retroactively without the consensus of the network. This ensures transparency, security, and trust among participants. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block, forming an unbreakable link between them. By decentralizing control and enabling peer-to-peer interactions, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize industries beyond finance, including supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and immutability through cryptographic linking of data blocks.
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications across various sectors, primarily due to its ability to provide transparency, security, and decentralization. In finance, blockchain facilitates secure transactions and enables the creation of cryptocurrencies, while in supply chain management, it enhances traceability and accountability by allowing stakeholders to track products from origin to consumer. Healthcare benefits from blockchain through secure patient data sharing and improved interoperability among systems. Additionally, the technology is being explored for use in voting systems, digital identity verification, and intellectual property protection, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize traditional processes and enhance trust in digital interactions. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain's applications include secure financial transactions, supply chain traceability, healthcare data sharing, voting systems, digital identity verification, and intellectual property protection, enhancing transparency and trust across various industries.


Explaining blockchain technology presents several challenges due to its inherent complexity and the abstract nature of its concepts. Many people struggle to grasp the decentralized structure, cryptographic principles, and consensus mechanisms that underpin blockchain systems. Additionally, the technical jargon often used in discussions can alienate non-experts, making it difficult for them to understand how blockchain differs from traditional databases. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of blockchain applications, such as cryptocurrencies and smart contracts, adds another layer of confusion, as individuals may conflate these specific use cases with the broader technology itself. To effectively communicate the essence of blockchain, one must simplify the terminology, use relatable analogies, and focus on practical implications rather than just technical details. **Brief Answer:** The challenges of explaining blockchain stem from its complexity, abstract concepts, technical jargon, and rapidly evolving applications, which can confuse non-experts. Simplifying terminology and using relatable analogies can help bridge this understanding gap.
Building your own blockchain involves several key steps that require a solid understanding of distributed ledger technology. First, you need to define the purpose of your blockchain—whether it's for cryptocurrency, supply chain management, or another application. Next, choose a consensus mechanism (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) that suits your needs. After that, design the architecture, including how nodes will communicate and how data will be structured in blocks. You can then select a programming language (such as Python, JavaScript, or Go) to start coding the blockchain protocol. Implement security measures to protect against attacks, and finally, test your blockchain thoroughly before deploying it. Documentation is crucial throughout the process to ensure clarity and facilitate future updates. **Brief Answer:** To build your own blockchain, define its purpose, choose a consensus mechanism, design the architecture, select a programming language, implement security measures, and conduct thorough testing before deployment.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568