Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
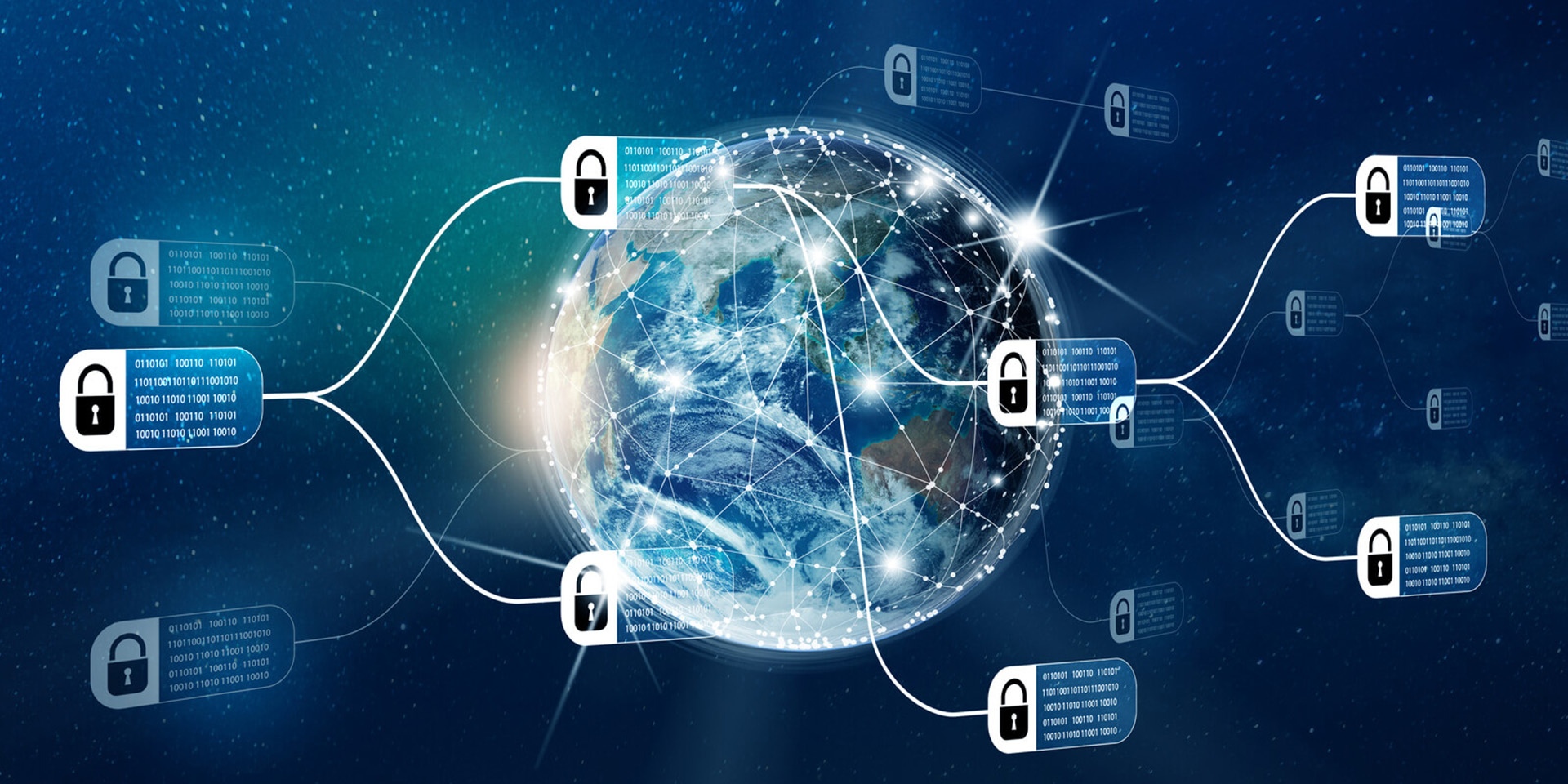

A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This ensures transparency and trust among participants, as each block of data is linked to the previous one, forming a chain. Each transaction is verified by network nodes through cryptography, making it resistant to fraud and tampering. Blockchains can be public, allowing anyone to participate, or private, restricted to specific users, and they serve as the foundational technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, as well as various applications in sectors such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare. **Brief Answer:** A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records and verifies transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and resistance to tampering.
The definition of a blockchain encompasses a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers. This foundational characteristic enables a wide array of applications across various sectors. In finance, blockchains facilitate secure and transparent transactions, enabling cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Supply chain management benefits from blockchain's ability to provide traceability and authenticity of goods, enhancing accountability among stakeholders. Additionally, in healthcare, patient records can be securely stored and shared, ensuring privacy while improving access to critical information. Other applications include smart contracts, which automate and enforce agreements without intermediaries, and voting systems that enhance transparency and reduce fraud. Overall, the versatility of blockchain technology is transforming industries by fostering trust, security, and efficiency. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain technology has diverse applications, including secure financial transactions (cryptocurrencies), supply chain traceability, healthcare data management, smart contracts, and transparent voting systems, all enhancing trust and efficiency across various sectors.


The definition of a blockchain presents several challenges due to its multifaceted nature and the rapid evolution of technology. At its core, a blockchain is often described as a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. However, variations in implementation—such as public versus private blockchains, consensus mechanisms, and governance structures—complicate this definition. Additionally, the integration of smart contracts and other functionalities further blurs the lines of what constitutes a blockchain. The lack of universally accepted terminology and standards also contributes to confusion, making it difficult for stakeholders to communicate effectively about the technology's capabilities and limitations. **Brief Answer:** The challenges in defining a blockchain stem from its diverse implementations, evolving features like smart contracts, and the absence of standardized terminology, leading to confusion among stakeholders regarding its capabilities and limitations.
Building your own definition of a blockchain involves understanding its core components and functionalities while considering its applications and implications. Start by researching the fundamental principles of blockchain technology, such as decentralization, transparency, immutability, and consensus mechanisms. Reflect on how these elements interact to create a secure and efficient system for recording transactions. Consider the various use cases beyond cryptocurrency, including supply chain management, healthcare, and digital identity verification. Finally, synthesize your insights into a concise definition that encapsulates both the technical aspects and the broader societal impact of blockchain technology, ensuring it resonates with your personal understanding and perspective. **Brief Answer:** To build your own definition of a blockchain, research its key features like decentralization and immutability, explore diverse applications, and synthesize your insights into a clear, personalized definition that reflects both its technical and societal significance.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568