Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
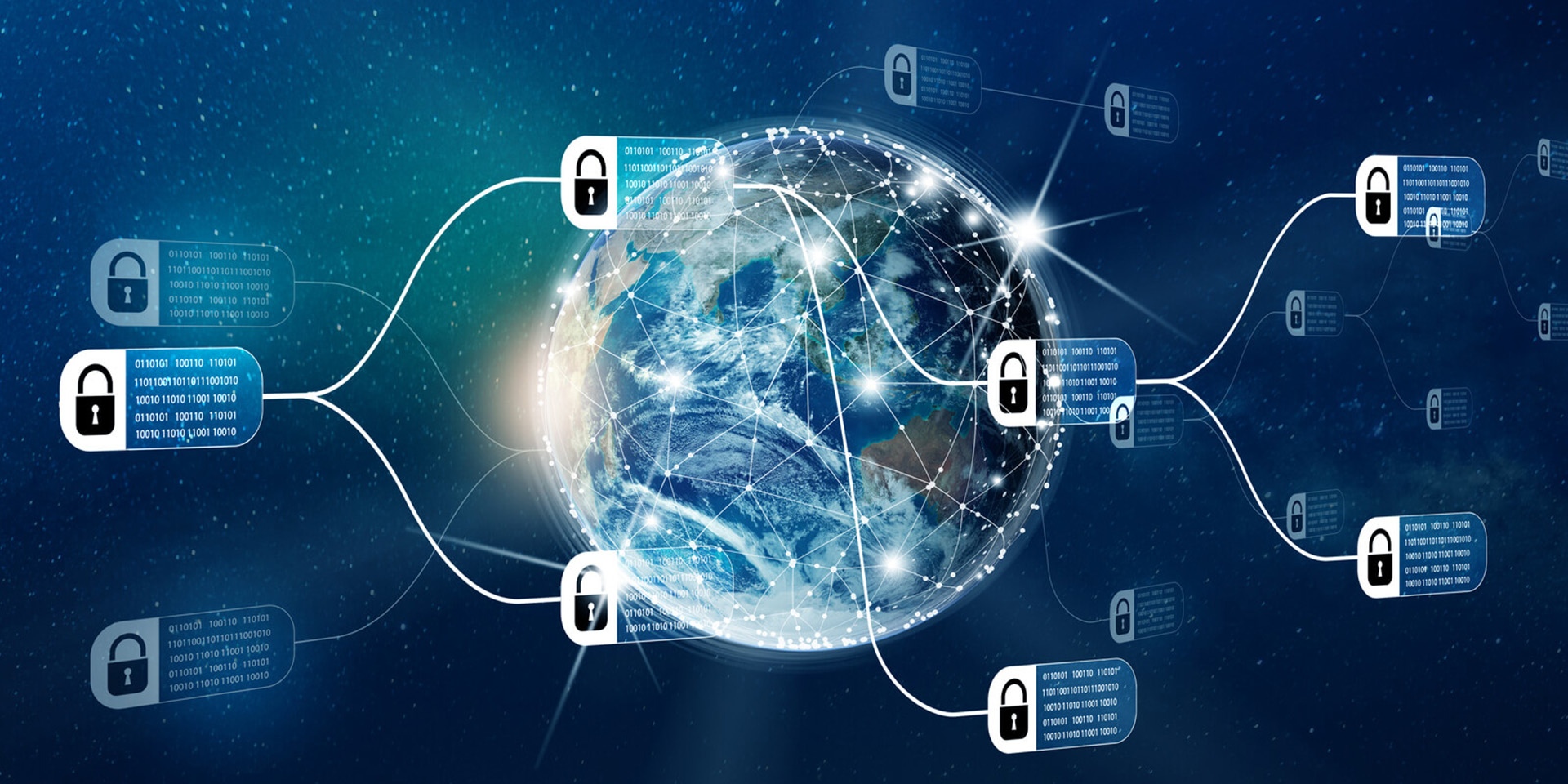

Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This ensures transparency and trust among participants without the need for a central authority. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block, linking them together in chronological order. The distributed nature of blockchain makes it resistant to fraud and tampering, making it a foundational technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, as well as various applications in supply chain management, healthcare, finance, and more. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records and verifies transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and resistance to tampering without a central authority.
Applications of blockchain technology extend far beyond its initial use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Today, it is being utilized across various sectors to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. In supply chain management, blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. In finance, it facilitates faster and more secure transactions while minimizing the need for intermediaries. Healthcare leverages blockchain for secure patient data sharing, enhancing privacy and interoperability. Additionally, smart contracts automate and enforce agreements without the need for third parties, streamlining processes in industries such as real estate and legal services. Overall, blockchain's decentralized nature offers innovative solutions to complex problems across multiple domains. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain applications include supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and smart contracts, enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency across various sectors.


The challenges of blockchain technology encompass a range of technical, regulatory, and societal issues that hinder its widespread adoption. One significant challenge is scalability; as the number of transactions increases, many blockchain networks struggle to maintain speed and efficiency, leading to delays and higher transaction costs. Additionally, energy consumption is a critical concern, particularly for proof-of-work systems, which require substantial computational power. Regulatory uncertainty also poses a challenge, as governments grapple with how to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies and blockchain applications. Furthermore, security vulnerabilities, such as smart contract bugs and potential attacks on network integrity, remain prevalent. Lastly, user education and understanding are essential for broader acceptance, as many individuals still lack familiarity with blockchain technology. **Brief Answer:** The challenges of blockchain include scalability issues, high energy consumption, regulatory uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and the need for greater user education.
Building your own blockchain involves several key steps that require a solid understanding of distributed ledger technology. First, you need to define the purpose and use case for your blockchain, whether it's for cryptocurrency, supply chain management, or another application. Next, choose the consensus mechanism that will govern how transactions are validated—options include Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or others. After that, you'll need to design the architecture, including deciding whether it will be public or private, and what kind of data structure you'll use. Then, you can start coding the blockchain using programming languages like Solidity for Ethereum-based projects or Python for custom solutions. Finally, test your blockchain thoroughly to ensure security and functionality before deploying it to a live environment. In brief, building your own blockchain requires defining its purpose, selecting a consensus mechanism, designing the architecture, coding, and thorough testing before deployment.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568