Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
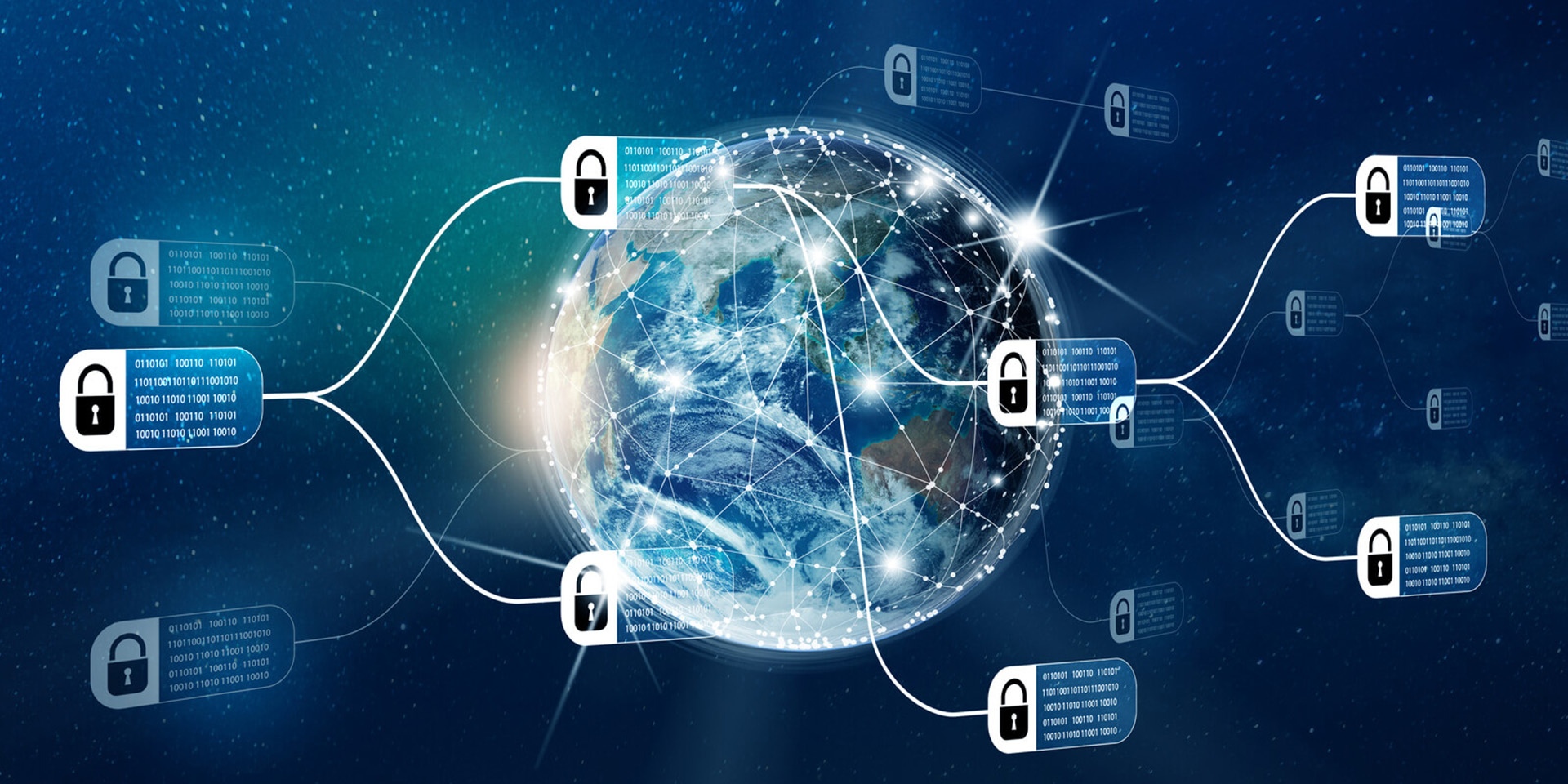

Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that the data cannot be altered retroactively without the consensus of the network. An example of blockchain in action is Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, which utilizes blockchain to maintain a transparent and tamper-proof record of all transactions. Each transaction is grouped into blocks, which are then linked together in chronological order, forming a chain. This structure not only enhances security but also fosters trust among users, as everyone on the network can verify the authenticity of transactions without relying on a central authority.
Blockchain technology has a wide range of applications across various industries, revolutionizing how data is stored, shared, and secured. One prominent example is in supply chain management, where blockchain provides transparency and traceability for products as they move through the supply chain. Companies can record every transaction on a decentralized ledger, allowing stakeholders to verify the authenticity and origin of goods. This not only enhances trust among consumers but also helps in identifying inefficiencies and reducing fraud. Other notable applications include financial services, where cryptocurrencies and smart contracts streamline transactions, and healthcare, where patient records can be securely shared while maintaining privacy. Overall, blockchain's ability to create immutable records and facilitate peer-to-peer interactions makes it a transformative technology across multiple sectors.


One of the significant challenges of blockchain technology is scalability. As more users join a blockchain network, the volume of transactions increases, leading to slower processing times and higher fees. For instance, during peak usage periods, networks like Ethereum have experienced congestion, resulting in delays and increased costs for users trying to execute transactions. Additionally, the energy consumption associated with proof-of-work consensus mechanisms poses environmental concerns, while regulatory uncertainty can hinder widespread adoption. These challenges highlight the need for ongoing innovation and development within the blockchain space to enhance its efficiency and sustainability. **Brief Answer:** The challenges of blockchain include scalability issues, high energy consumption, and regulatory uncertainty, which can impede transaction speed, increase costs, and limit adoption.
Building your own blockchain involves several key steps that require a solid understanding of distributed ledger technology. First, you need to define the purpose of your blockchain and its consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Next, choose a programming language (like Python, JavaScript, or Go) to develop the blockchain's core functionalities, including transaction handling, block creation, and network protocols. You will then set up nodes that will participate in the network, ensuring they can communicate with each other. After implementing the basic structure, test your blockchain thoroughly for security and performance issues. Finally, deploy your blockchain on a network and invite users to join, ensuring you have a clear governance model in place for future updates and decision-making. **Brief Answer:** To build your own blockchain, define its purpose and consensus mechanism, choose a programming language, develop core functionalities, set up communicating nodes, test for security, and deploy it on a network with a governance model.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568