Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
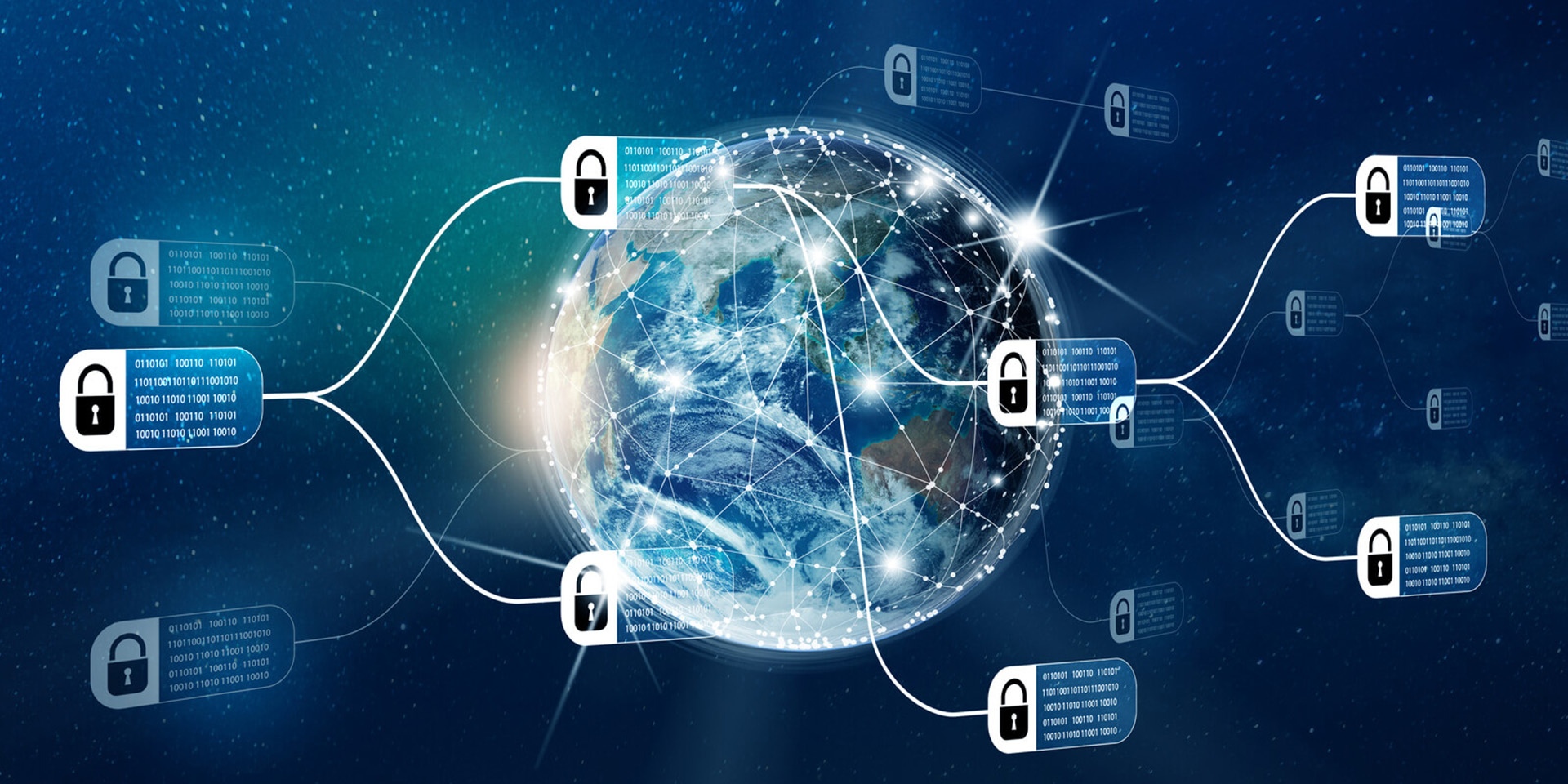

Blockchain cryptography refers to the use of cryptographic techniques to secure and validate transactions within a blockchain network. At its core, blockchain technology relies on cryptographic algorithms to ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity. Each block in a blockchain contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an immutable chain that prevents tampering and fraud. Additionally, public-key cryptography is employed to facilitate secure transactions between users, allowing them to send and receive digital assets without the need for intermediaries. This combination of cryptographic methods not only enhances security but also fosters trust among participants in decentralized systems. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain cryptography uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and maintain data integrity in a blockchain network, ensuring that information is authentic and tamper-proof while enabling secure peer-to-peer interactions.
Blockchain cryptography has a wide array of applications that extend beyond cryptocurrencies. One of the most significant uses is in securing transactions and ensuring data integrity across various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. In finance, blockchain enables secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, reducing fraud risk. In supply chains, it enhances transparency by allowing all parties to track the provenance of goods in real-time. Additionally, in healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, ensuring privacy while allowing authorized access for medical professionals. Other applications include smart contracts, which automate and enforce agreements, and decentralized identity verification systems, which enhance security and reduce identity theft. Overall, blockchain cryptography provides a robust framework for enhancing trust and security in digital interactions. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain cryptography secures transactions and ensures data integrity across various sectors, including finance (peer-to-peer transactions), supply chain management (tracking goods), and healthcare (secure patient records). It also supports smart contracts and decentralized identity verification, enhancing trust and security in digital interactions.


Blockchain cryptography presents several challenges that can impact its effectiveness and adoption. One significant challenge is the scalability issue; as the number of transactions increases, the cryptographic processes required for validation can lead to slower transaction times and higher costs. Additionally, the complexity of cryptographic algorithms can make them vulnerable to attacks if not implemented correctly, raising concerns about security. Furthermore, the immutability of blockchain means that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, which poses a challenge in cases of erroneous entries or fraud. Lastly, the energy consumption associated with certain consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work, raises environmental concerns, prompting the need for more sustainable alternatives. **Brief Answer:** The challenges of blockchain cryptography include scalability issues, potential vulnerabilities in complex algorithms, immutability leading to difficulties in correcting errors, and high energy consumption from certain consensus mechanisms.
Building your own blockchain cryptography involves several key steps that integrate both theoretical knowledge and practical implementation. First, you need to understand the fundamental concepts of blockchain technology, including decentralized networks, consensus algorithms, and cryptographic principles such as hashing and public-private key pairs. Next, choose a programming language (like Python, JavaScript, or Go) to develop your blockchain. Start by creating a data structure for blocks that includes transaction data, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block's hash. Implement a hashing function (e.g., SHA-256) to secure each block and ensure data integrity. Then, establish a consensus mechanism (such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to validate transactions across the network. Finally, test your blockchain thoroughly to identify vulnerabilities and optimize performance before deploying it in a live environment. **Brief Answer:** To build your own blockchain cryptography, learn the basics of blockchain and cryptography, choose a programming language, create a block structure with hashing for security, implement a consensus mechanism, and rigorously test your system before deployment.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568