Blockchain: The Revolution in Data Security and Transparency
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
Transforming Industries with Decentralized Solutions
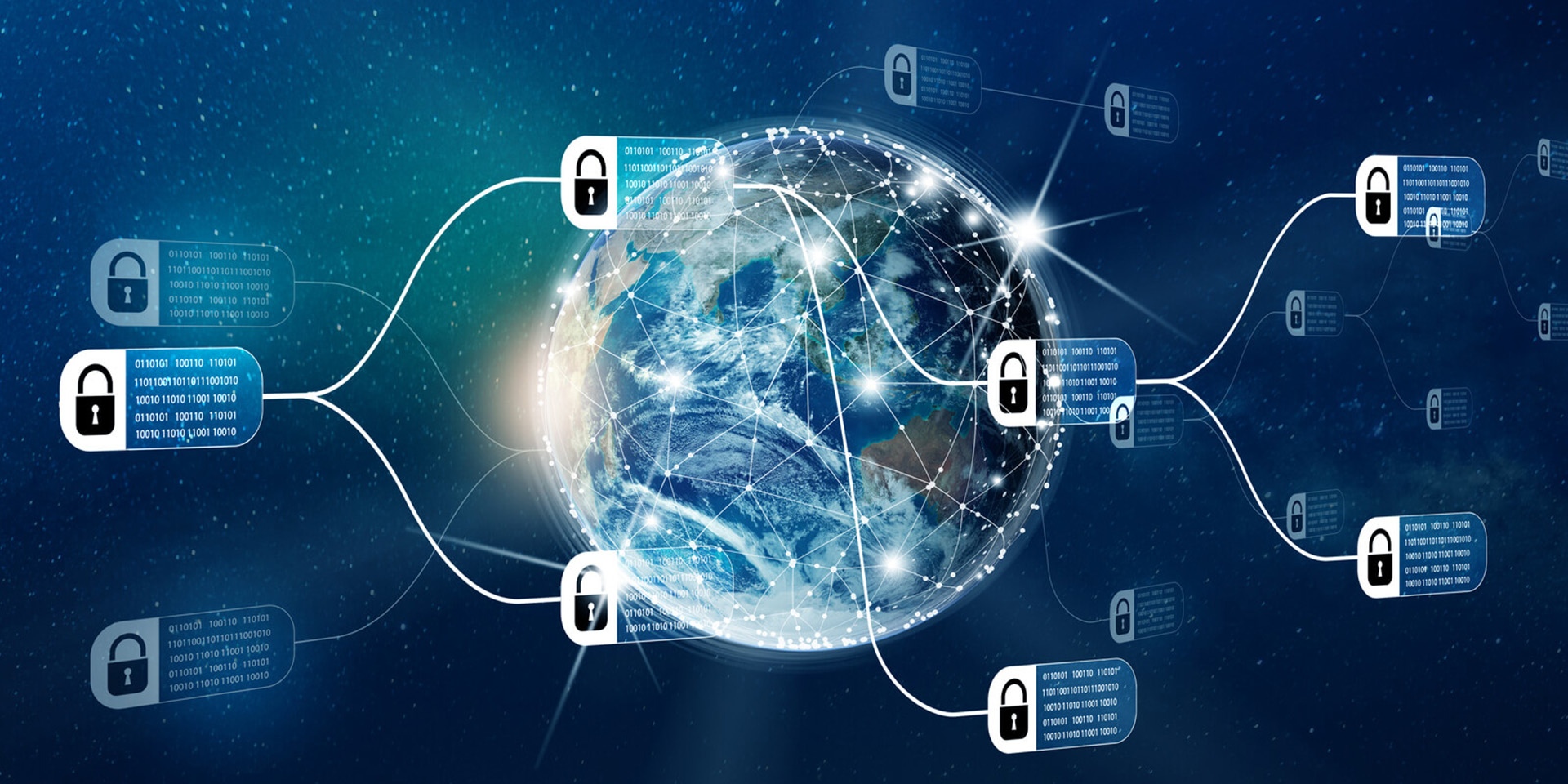

Blockchain architecture refers to the structural design of a blockchain system, encompassing its components, protocols, and processes that enable decentralized data storage and transaction management. At its core, blockchain architecture consists of three main layers: the network layer, which facilitates peer-to-peer communication; the protocol layer, which defines the rules for data validation and consensus mechanisms; and the application layer, where user-facing applications interact with the blockchain. This architecture ensures transparency, security, and immutability by distributing data across a network of nodes, making it resistant to tampering and fraud. Overall, blockchain architecture is fundamental to the functioning of various applications, from cryptocurrencies to supply chain management. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain architecture is the structural design of a blockchain system, comprising layers that facilitate decentralized data storage and transaction management, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability through distributed networks.
Blockchain architecture has a wide range of applications across various industries due to its inherent characteristics of decentralization, transparency, and security. In finance, it enables secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Supply chain management benefits from blockchain by providing real-time tracking of goods, enhancing traceability, and ensuring authenticity. In healthcare, patient records can be securely stored and shared among authorized parties, improving data integrity and patient care. Additionally, blockchain is utilized in voting systems to enhance transparency and reduce fraud, as well as in digital identity verification to protect personal information. Overall, the versatility of blockchain technology continues to drive innovation and improve processes in numerous sectors. **Brief Answer:** Blockchain architecture is applied in finance for secure transactions, in supply chain management for tracking goods, in healthcare for secure patient records, in voting systems for transparency, and in digital identity verification, showcasing its versatility and potential to enhance various industries.


Blockchain architecture presents several challenges that can hinder its widespread adoption and efficiency. One significant issue is scalability; as the number of transactions increases, the network can become congested, leading to slower processing times and higher transaction fees. Additionally, energy consumption is a critical concern, particularly for proof-of-work systems, which require substantial computational power. Security vulnerabilities, such as potential attacks on smart contracts or consensus mechanisms, also pose risks. Furthermore, regulatory uncertainties and interoperability between different blockchain networks complicate integration into existing systems. These challenges necessitate ongoing research and innovation to enhance blockchain's functionality and usability. **Brief Answer:** The challenges of blockchain architecture include scalability issues, high energy consumption, security vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties, and difficulties in interoperability, all of which need to be addressed for broader adoption and efficiency.
Building your own blockchain architecture involves several key steps that require careful planning and technical expertise. First, define the purpose of your blockchain—whether it's for cryptocurrency, supply chain management, or another application. Next, choose the consensus mechanism that best fits your needs, such as Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or Delegated Proof of Stake. After that, design the network structure, deciding whether it will be public, private, or consortium-based. Then, select the appropriate technology stack, including programming languages and frameworks, to develop the blockchain. Finally, implement security measures, conduct thorough testing, and deploy your blockchain while ensuring scalability and interoperability with existing systems. **Brief Answer:** To build your own blockchain architecture, define its purpose, choose a suitable consensus mechanism, design the network structure, select the technology stack, implement security measures, and thoroughly test before deployment.
Easiio stands at the forefront of technological innovation, offering a comprehensive suite of software development services tailored to meet the demands of today's digital landscape. Our expertise spans across advanced domains such as Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Large Language Model (LLM) applications, and sophisticated algorithms. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, Easiio crafts bespoke solutions that drive business success and efficiency. To explore our offerings or to initiate a service request, we invite you to visit our software development page.



TEL:866-460-7666
EMAIL:contact@easiio.com
ADD.:11501 Dublin Blvd. Suite 200, Dublin, CA, 94568